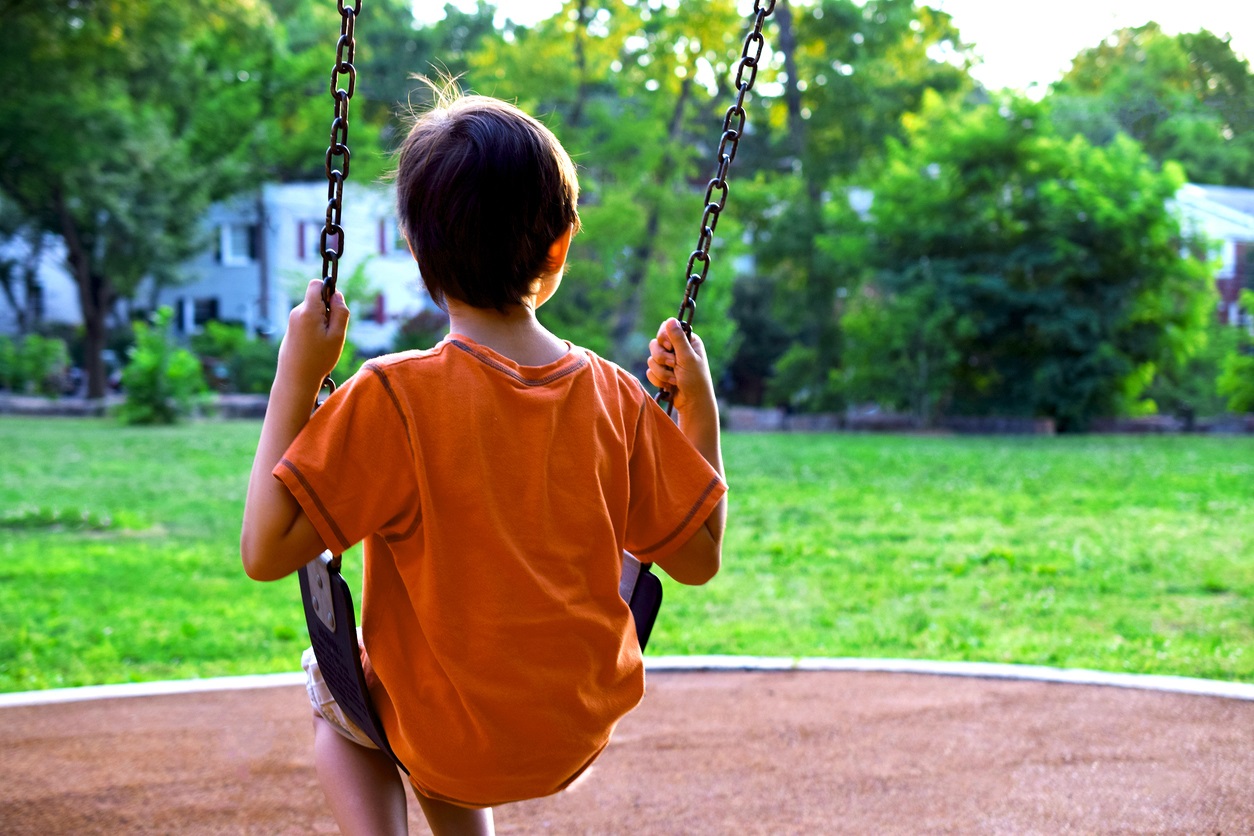
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common chronic health disorders in school-aged children. Children with ADHD are hyperactive, have trouble staying focused, and struggle to manage their behavior.
Individuals with ADHD may be at twice the risk of sustaining traumatic dental injuries (TDIs). Some of the most common TDI’s are broken teeth, knocked-out teeth, and dislodged teeth.
While the most common causes of TDIs have been identified as playground or sports accidents, a well-known feature of ADHD is accident proneness. Violence, another significant risk factor for TDIs, is more likely to be observed in conduct disorder, a common comorbidity (the presence of two or more medical conditions) of ADHD.
Early identification and intervention for ADHD can reduce the risk of TDIs.
In a systemic review of 12 studies, published in the European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, the analysis revealed that individuals with ADHD have roughly 2 times higher odds of experiencing TDI’s compared to those without ADHD.
The findings highlight the functional impairments associated with ADHD, such as disrupted motor coordination and difficulties in forming peer connections.
This review did have limitations, such as a small sample size and the varying ages of participants (ranging from 7 to 17), but it provides insights and awareness to the association between TDI’s and individuals with ADHD.
Leave a reply →